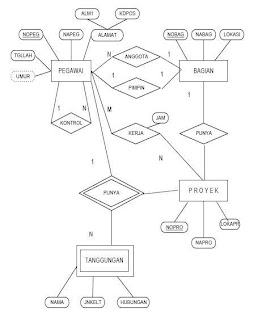
MAPPING OF ER-DIAGRAM :
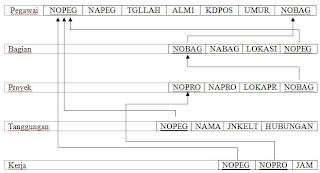
NORMALIZATION OF MAPPING :
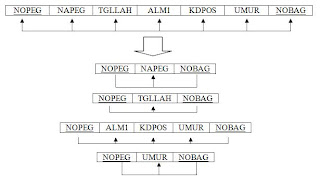
Pegawai :
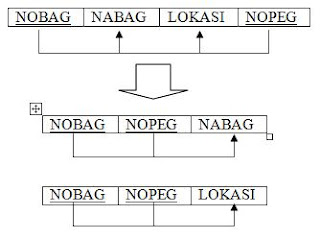
Bagian :
Proyek :
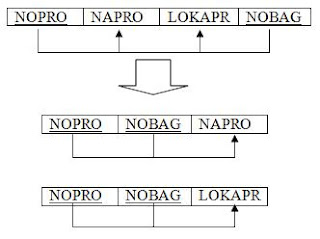
Tanggungan :

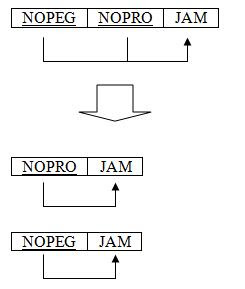
Kerja :








1. Pentingnya Pengembangan Sistem Informasi
a. Adanya permasalahan – permasalahan (problem) yang timbul di sistem yang lama. Permasalahan yang timbul dapat berupa:
- Kecurangan – kecurangan disengaja yang menyebabkan tidak amannya harta kekayaan perusahaan dan kebenaran dari data menjadi kurang terjamin.
- Kesalahan – kesalahan yang tidak disengaja yang juga dapat menyebabkan kebenaran dari data kurang terjamin.
- Tidak efisiennya operasi.
- Tidak ditaatinya kebijaksanaan manajemen yang telah ditetapkan.
b. Pertumbuhan Organisasi yang menyebabkan harus disusunnya sistem yang baru. Pertumbuhan organisasi diantaranya adalah kebutuhan informasi yang semakin luas, volume pengolahan data semakin meningkat, perubahan prinsip akuntansi yang baru. Karena adanya perubahan ini, maka menyebabkan sistem yang lama tidak efektif lagi, sehingga sistem yang lama sudah tidak dapat memenuhi lagi kebutuhan informasi yang dibutuhkan manajemen.
c. Untuk meraih kesempatan – kesempatan (oppotunities).
Teknologi informasi telah berkembang dengan cepat. Teknologi informasi telah berkembang dengan cepat. Perangkat keras komputer, perangkat lunak, dan teknologi komunikasi telah begitu cepat berkembang. Organisasi mulai merasakan bahwa teknologi informasi ini perlu digunakan untuk meningkatkan penyediaan informasi sehingga dapat mendukung dalam proses pengambilan keputusan yang akan dilakukan oleh manajemen.
d. Adanya instruksi – instruksi (directives)
Penyusunan sistem yang baru dapat juga terjadi karena adanya instruksi – instruksi dari atas pimpinan ataupun dari luar organisasi seperti misalnya peraturan pemerintah.
2. Tujuan Pengembangan Sistem Informasi
- Memecahkan permasalahan – permasalahan
- Meraih kesempatan – kesempatan
- Memenuhi instruksi yang diberikan
3. Harapan Informasi Setelah Menerapkan Sistem Informasi
a. Performance (Kinerja)
- Diukur menggunakan throughput dan response time
b. Information (Informasi)
- Peningkatan kualitas informasi
c. Economy (Ekonomis)
- Peningkataan manfaat vs penurunan biaya
d. Control (Pengendalian)
- Mendeteksi dan memperbaiki kesalahan
e. Efficiency (Efisiensi)
- Efisien operasional
f. Services (Pelayanan)
- Peningkatan pelayanan sistem
4. Prinsip Pengembangan Sistem Informasi
a. Sistem yang dikembangkan adalah untuk manajemen.
b. Sistem yang dikembangkan adalah investasi modal yang besar.
c. Sistem yang dikembangkan memerlukan orang yang terdidik.
d. Tahapan kerja dan tugas – tugas yang harus dilakukan dalam proses pengembangan sistem.
e. Proses pengembangan sistem tidak harus urut.
f. Jangan tekut membatalkan proyek.
g. Dokumentasi harus ada untuk pedoman dalam pengembangan sistem.
5. Pengembangan Sistem Life Cycle Models
a. Model Waterfall
Pada model ini dilakukan dengan proses tahap demi tahap yang dilalui harus menunggu selesainya tahap sebelumnya dan berjalan berurutan. Sebagai contoh tahap desain harus menunggu selesainya tahap sebelumnya yaitu tahap requipment. Secara umum tahapan pada model waterfall dapat dilihat pada gambar berikut:
Pressman memecah model ini menjadi enam tahapan meskipun secara garis besar sama dengan tahapan – tahapan model waterfall pada umumnya. Berikut adalah penjelasan dari tahap – tahap yang dilakukan dalam model ini menurut pressman:
- Sistem/Information Engineering and Modeling
Pemodelan ini diawali dengan mencari kebutuhan dari keseluruhan system yang akan diaplikasikan dalam bentuk software.
- Software Requipments Analysis
Proses pencarian kebutuhan diintesifkan dan difokuskan pada software. Untuk mengetahui sifat program yang akan dibuat maka pada software engineer harus mengerti tentang domain informasi dari software, misalnya fungsi yang dibutuhkan, user interface. Dari dua aktifitas tersebut harus didokumentasikan dan ditunjukkan pada pelanggan.
- Design
Proses ini digunakan untuk mengubah kebutuhan-kebutuhan diatas menjadi representasi ke dalam bentuk “blueprint” software sebelum coding dimulai. Desain harus dapat mengimplementasikan kebutuhan yang telah disebutkan pada tahap sebelumnya. Seperti 2 aktivitas sebelumnya, maka proses ini juga harus didokumentasikan sebagai konfigurasi dari software.
- Coding
Untuk dapat dimengerti oleh mesin, dalam hal ini adalah komputer, maka desain tadi harus diubah bentuknya menjadi bentuk yang dapat dimengerti oleh mesin, yaitu ke dalam bahasa pemrograman melalui proses coding. Tahap ini merupakan implementasi dari tahap design yang secara teknis nantinya dikerjakan oleh programmer.
- Testing/Verification
Sesuatu yang dibuat haruslah diujicobakan. Demikian juga dengan software. Semua fungsi-fungsi software harus diujicobakan, agar software bebas dari error, dan hasilnya harus benar-benar sesuai dengan kebutuhan yang sudah didefinisikan sebelumnya.
- Maintenance
Pemeliharaan suatu software diperlukan, termasuk di dalamnya adalah pengembangan, karena software yang dibuat tidak selamanya hanya seperti itu. Ketika dijalankan mungkin saja masih ada errors kecil yang tidak ditemukan sebelumnya, atau ada penambahan fitur-fitur yang belum ada pada software tersebut. Pengembangan diperlukan ketika adanya perubahan dari eksternal perusahaan seperti ketika ada pergantian sistem operasi, atau perangkat lainnya.
Sumber :
http://hansiaditya.wordpress.com/2007/09/25/waterfall-process-model/
b. Model Iteratif
Model inkremental menggabungkan elemen-elemen model waterfall (diaplikasikan secara berulang) dengan prototipe iteratif. Model ini memakai urutan-urutan linier dalam model seiring dengan laju waktu. Setiap urutan linier menghasilkan pertambahan perangkat lunak. Pada saat model pertambahan dipergunakan, pertambahan pertama seringkali adalah produk inti. Produk inti ini kemudian dipergunakan oleh pelanggan. Sebagai hasil dari pemakaian dan/atau evaluasi, prototipe dikembangkan untuk pertambahan selanjutnya. Prototipe tersebut menekankan modifikasi produk inti agar dapat memenuhi kebutuhan pelanggan dan fitur serta fungsionalitas tambahan. Model inkremental ini seperti model prototipe dan pendekatan-pendekatan evolusioner lain yang bersifat iteratif. Tetapi tidak seperti model prototipe, model inkremental berfokus pada penyampaian produk operasional dalam setiap pertambahannya. Pertambahan awal ada di versi striped down dari produk akhir, tetapi memberikan kemampuan untuk melayani pemakai dan juga menyediakan platform untuk evaluasi oleh pemakai. Perkembangan incremental berguna pada saat staffing tidak dapat digunakan untuk batas waktu bisnis yang telah ditetapkan untuk proyek tersebut. Jika produk inti diterima, maka staf tambahan bisa ditambahkan untuk mengimplementasikan pertambahan selanjutnya.
c. Model Spiral
Merupakan model proses perangkat lunak evolusioner yang merangkai sifat iterative dari prototype dengan cara control dan aspek sistematis model sequensial linier.
Tahapan – tahapan model spiral :
- Komunikasi Pelanggan, merupakan tugas – tugas untuk membangun komunikasi antara pelanggan dan kebutuhan – kebutuhan yang idiinginkan oleh pelanggan.
- Perencanaan, merupakan tugas – tugas untuk mendefinisikan sumber daya, ketepatan waktu dan proyek informasi lain yang berhubungan.
- Analisis Resiko, merupakan tugas yang dibutuhkan untuk menaksir resiko manajemen dan teknis.
- Perekayasaan, merupakan tugas yang dibuthkan untuk membangun satu atau lebih representasi dari aplikasi tersebut.
- Konstruksi dan peluncuran, merupakan tugas – tugas yang dibutuhkan untuk mengkontruksi, menguji, memasang, dan memberi pelayanan kepada pemakai.
6. Pendekatan Dari Pengembangan Sistem
Terdapat beberapa pendekatan untuk mengembangkan sistem, yaitu sebagai berikut :
a. Pendekatan klasik lawan pendekatan terstruktur
- Pendekatan klasik
Tahapan – tahapan dalam SDLC. Tidak mengikutsertakan pengguna, lebih menekankan analis sistem.
- Pendekatan terstruktur
Pengguna terlibat dari awal untuk menentukan kebutuhan sistem. Menggunakan tools – tools seperti data flow diagram.
b. Pendekatan sepotong lawan pendekatan sistem
- Pendekatan sepotong
Menekankan pada suatu aplikasi atau kegiatan. Tidak mengindahkan sasaran keseluruhan.
- Pendekatan sistem
Melihat sistem sebagai satu kesatuan yang utuh. Menekankan pada pencapaian sasaran secara keseluruhan.
c. Pendekatan bawah-naik lawan pendekatan atas-turun
- Pendekatan bawah-naik
Dimulai dari level bawah yaitu operasional. Merupakan ciri – ciri pendekatan klasik. Dikenal dengan istilah data analysis.
- Pendekatan atas-turun
Dimulali dari level atas yaitu perencanaan strategi. Merupakan ciri – ciri pendekatan terstruktur. Dikenal juga dengan decision analysis.
d. Pendekatan sistem-menyeluruh lawan pendekatan moduler
- Pendekatan sistem-seluruh
Mengembangkan sistem secara serentak dan menyeluruh dan merupakan ciri – ciri pendekatan klasik.
- Pendekatan moduler
Memecahkan sistem yang rumit menjadi bagian – bagian yang sederhana. Sistem yang dikembangkan menjadi tepat waktu, mudah untuk dipahami, dan dipelihara. Merupakan ciri – ciri pendekatan terstruktur.
e. Pendekatan lompatan jauh lawan pendekatan berkembang
- Pendekatan lompatan jauh lawan
Mengembangkan sistem secara serentak menggunakan teknologi canggih. Beresiko tinggi dan menghabiskan banyak biaya.
- Pendekatan berkembang
Menerapkan teknologi canggih untuk aplikasi – aplikasi tertentu. Dikembangkan untuk mengikuti kebutuhan. Hemat biaya dan dapat mengikuti perkembangan teknologi.
7. Arti Dari Metodelogi, Metode, dan Algoritma
- Metodelogi merupakan metode – metode digunakan oleh suatu ilmu pengetahuan.
- Metode merupakan suatu cara sistematik untuk mengerjakan sesuatu.
- Algoritma merupakan urut – urutan prosedur untuk memecahkan suatu masalah
8. Tiga Klasifikasi Metodelogi Pengembangan
a. Functional decomposition methodologies.
Metodelogi ini menekankan pada pemecahan dari sistem kedalam subsistem – subsistem yang lebih kecil, sehingga akan lebih mudah untuk dipahami, dirancang dan diterapkan.
b. Data-oriented methodologies.
Metodelogi ini menekankan pada kearakteristik dari data yang akan diproses. Metodelogi ini dapat dikelompokkan menjadi dua kelas, yaitu:
- Data-flow oriented methodologies.
Metodelogi ini secara umum didasarkan pada pemecahan dari sistem kedalam modul – modul berdasarkan dari tipe elemen data dan tingkah laku logika modul tersebut didalam sistem. Dengan metodelogi ini, sistem secara logika dapat digambarkan secara logika dari arus data dan hubungan antar fungsinya didalam modul – modul di sistem.
- Data structure oriented methodologies.
Metodelogi ini menekankan struktur dari input dan output di sistem. Struktur ini kemudian akan digunakan sebagai dasar struktur dari sistemnya. Hubungan fungsi antar modul atau elemen – elemen sistem kemudian dijelaskan dari struktur sistemnya.
c. Prescriptive Methodologies.
Biasanya disediakan oleh pabrik pembuat perangkat lunak.
9. Teknik Penggunaan Dalam Pengembangan Sistem
a. Teknik manajemen proyek, yaitu CPM (Critical Path Method) dan PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique). Teknik ini digunakan untuk penjadualan proyek.
b. Teknik menemukan fakta (Fact finding techniques), yaitu teknik yang dapat digunakan untuk mengumpulkan data dan menemukan fakta – fakta dalam kegiatan mempelajari sistem yang ada. Teknik – teknik diantaranya adalah:
- Wawancara (interview)
- Observasi (Observation)
- Daftar pertanyaan (questionaires)
- Pengumpulan sample (sampling)
c. Teknik analisis biaya/mafaat (cost-effectiveness analysis dan cost-benefit analysis).
d. Teknik untuk menjalankan rapat.
e. Teknik inspeksi/walkthrough.
10. Perbedaan antara Analis Sistem dan Pemrogram.
- Analis Sistem adalah mempelajari masalah – masalah dan menentukan kebutuhan pemakai sistem untuk mengidentifikasikan pemecahan.
- Pemrogram adalah menulis kode program berdasarkan rancang bangun yang dibuat oleh analis.